The Enneagram: A Personality Model With Spiritual Connotations
The Enneagram is a personality typing system that categorizes individuals into nine distinct types, each representing different motivations, fears, and behavioral patterns. This model is not only used for understanding personality but also has deep spiritual implications and connotations.
Origins of the Enneagram
The origins of the Enneagram can be traced back to various philosophical and spiritual traditions, including early Christian mysticism. The contemporary understanding of the Enneagram was significantly shaped by figures such as Oscar Ichazo and Claudio Naranjo in the mid-20th century. The structure of the Enneagram consists of a geometric figure that illustrates how these nine types are interconnected. Each type is associated with specific emotional responses and coping mechanisms.
Spiritual Dimensions of the Enneagram
One of the key aspects that set the Enneagram apart from other personality models is its integration with spiritual growth. Each type reflects an aspect of divine nature, suggesting that understanding one’s type can lead to greater self-awareness and a deeper connection with God or a higher power. For instance, Type 1 (the Perfectionist) embodies God’s goodness, while Type 2 (the Helper) reflects God’s love.
Personal Growth Through Self-Awareness
The process of identifying one’s Enneagram type serves as a pathway for personal development. By recognizing their core beliefs and motivations, individuals can begin to untangle unhealthy patterns that may have developed over time due to life experiences or family dynamics. This journey often involves confronting uncomfortable truths about oneself, which can lead to significant transformation.
The Structure of the Enneagram
The Enneagram is visually represented as a nine-pointed geometric figure, which consists of a circle with nine equidistant points around its circumference. Each point corresponds to one of the nine personality types.
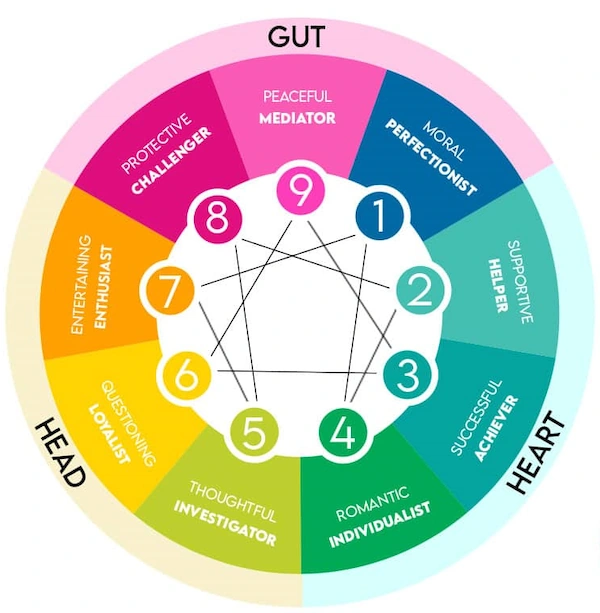
Type One: The Perfectionist
Type Ones are principled, purposeful, and self-disciplined individuals who strive for integrity and improvement. They have a strong sense of right and wrong and often hold themselves to high standards. Their motivation is driven by a desire to avoid mistakes and be morally good, which can lead them to be critical of themselves and others. They tend to see the world in black-and-white terms, making them appear rigid or inflexible.
Strengths: Ethical, dedicated, reliable, organized.
Faults: Critical, judgmental, can be overly controlling.
Basic Fear: Being corrupt or evil.
Basic Desire: To be good and have integrity.
Type Two: The Helper
Type Twos are caring, interpersonal individuals who thrive on being needed. They are empathetic and often prioritize the needs of others over their own. Their motivation stems from a deep-seated need for love and appreciation, which can lead them to become overly involved in the lives of others while neglecting their own boundaries.
Strengths: Warm-hearted, generous, supportive.
Faults: Overly accommodating; may struggle with self-neglect.
Basic Fear: Being unworthy of love.
Basic Desire: To feel loved.
Type Three: The Achiever
Type Threes are success-oriented individuals who seek validation through accomplishments. They are highly driven and focus on image management; they often equate their self-worth with their achievements. This can lead them to prioritize appearance over authenticity and may cause feelings of inadequacy when they do not meet their goals.
Strengths: Adaptable, goal-oriented, charismatic.
Faults: Overly focused on image; may lack authenticity.
Basic Fear: Being worthless or insignificant.
Basic Desire: To feel valuable.
Type Four: The Individualist
Type Fours are introspective and sensitive individuals who seek identity through uniqueness. They value deep emotional experiences and often feel different from others. Their quest for meaning can lead them into moodiness or feelings of inadequacy as they grapple with their emotions.
Strengths: Creative, emotionally aware, authentic.
Faults: Can be self-absorbed or moody; may struggle with envy.
Basic Fear: Having no identity or personal significance.
Basic Desire: To find meaning based on inner experience.
Type Five: The Investigator
Type Fives are analytical thinkers who prioritize knowledge and understanding. They tend to withdraw from social interactions to conserve energy for intellectual pursuits. Their independence can sometimes come off as aloofness or detachment from emotional connections.
Strengths: Insightful, perceptive, innovative.
Faults: Withdrawn; struggles with emotional expression.
Basic Fear: Being useless or helpless.
Basic Desire: To be competent.
Type Six: The Loyalist
Type Sixes are committed individuals who value security and loyalty. They often anticipate worst-case scenarios due to anxiety about safety and support. This vigilance makes them responsible but can also lead to self-doubt if they feel unsupported by others.
Strengths: Responsible, loyal, practical.
Faults: Anxious; may struggle with indecision or trust issues.
Basic Fear: Being without security or support.
Basic Desire: To have security.
Type Seven: The Enthusiast
Type Sevens are adventurous individuals who seek happiness through new experiences. They avoid emotional pain by staying busy with activities that bring joy but may struggle with commitment due to fear of confinement or boredom.
Strengths: Spontaneous, versatile, optimistic.
Faults: Scattered; may overextend themselves in pursuit of pleasure.
Basic Fear: Feeling trapped or experiencing pain.
Basic Desire: To be happy.
Type Eight: The Challenger
Type Eights are assertive leaders who seek control over their environment. They value strength and resilience but can come off as confrontational when asserting their will. Their protective nature drives them to stand up for those they perceive as weaker than themselves.
Strengths: Direct, resourceful, protective.
Faults: Controlling; may struggle with vulnerability or tenderness.
Basic Fear: Being harmed or controlled by others.
Basic Desire: To protect themselves and others.
Type Nine: The Mediator
Type Nines are easygoing individuals who prioritize harmony in relationships. They avoid conflict at all costs but may become complacent in doing so. Their desire for peace can lead them to neglect their own needs until they reach a breaking point where they might express suppressed anger unexpectedly.
Strengths: Accommodating, calm, genuine listeners.
Faults: Can become too complacent; may suppress anger until it explodes unexpectedly.
Basic Fear: Being disconnected or lost within themselves or in relationships with others.
Basic Desire: To have peace in their internal world.
Questo articolo in Italiano:


Comments
Post a Comment